Functional Nanoparticles
Functionalization Of Nanoparticles
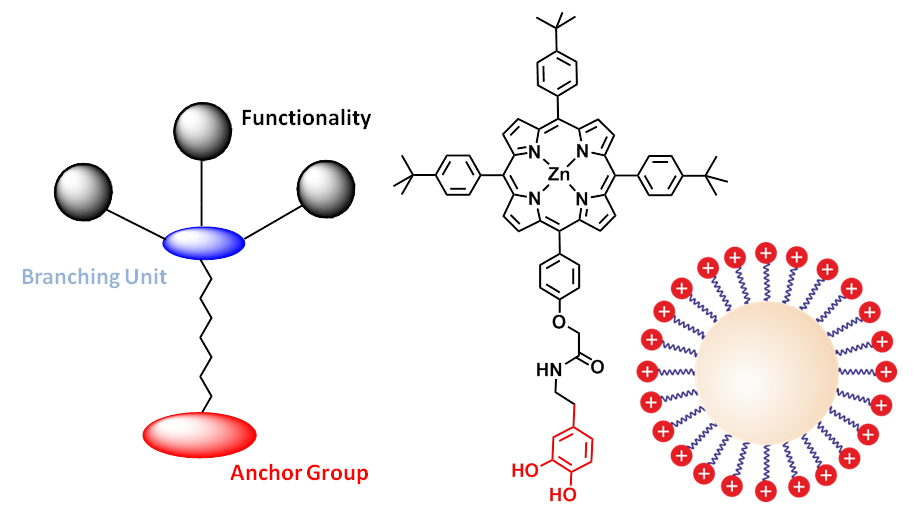
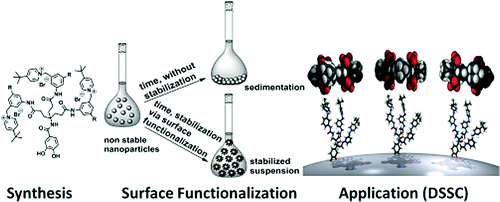
We are investigating the controlled chemical functionalization of inorganic nanoparticles (NP) such as ZnO-, TiO2-, Ag- and Au quantum dots and ZnO nanorods with organic building blocks. The latter include neutral and charged dendrimers, porphyrines and H-bonding architectures such as cyanuric acid derivatives and Hamiliton receptors. In this way we are able to improve the stability and dispersibility of the nanoparticles and control their supramolecular aggregation including layer-by-layer assembly on surfaces. The chemical derivatization of the nanoparticles with redox-active molecules and light-harvesting antennas is also important for their mplemention into optoelectronic applications.
Selected Publications
- , , , , , , :
Experimental and Theoretical Studies of the Colloidal Stability of Nanoparticles−A General Interpretation Based on Stability Maps
In: Acs Nano 5 (2011), p. 4658-4669
ISSN: 1936-0851
DOI: 10.1021/nn200465b
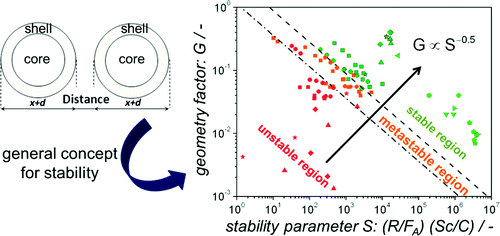
The current work addresses the understanding of the stabilization of nanoparticles in suspension. Specifically, we study ZnO in ethanol for which the influence of particle size and reactant ratio as well as surface coverage on colloidal stability in dependence of the purification progress was investigated. The results revealed that the well-known ζ-potential determines not only the colloidal stability but also the surface coverage of acetate groups bound to the particle surface. The acetate groups act as molecular spacers between the nanoparticles and prevent agglomeration. Next to DLVO calculations based on the theory of Derjaguin, Landau, Verwey and Overbeek using a core–shell model we find that the stability is better understood in terms of dimensionless numbers which represent attractive forces as well as electrostatic repulsion, steric effects, transport properties, and particle concentration. containers.
- , , , , , , , :
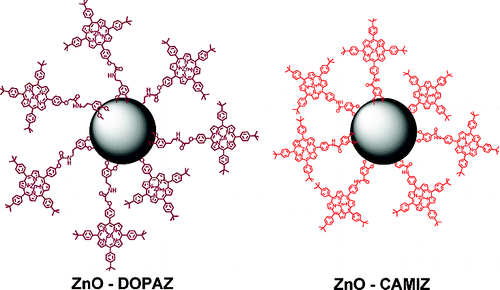
Efficient synthetic access to cationic dendrons and their application for ZnO nanoparticles surface functionalization: New building blocks for dye-sensitized solar cells
In: Journal of the American Chemical Society 132 (2010), p. 17910-17920
ISSN: 0002-7863
DOI: 10.1021/ja106076h
A new concept for the efficient synthesis of cationic dendrons, 4-tert-butyl-1-(3-(3,4-dihydroxybenzamido)benzyl)pyridinium bromide (17), 1,1′-(5-(3,4-dihydroxybenzamido)-1,3-phenylene)bis(methylene)bis(4-tert-butylpyridinium) bromide (18), N1,N7-bis(3-(4-tert-butyl-pyridium-methyl)phenyl)-4-(3-(3-(4-tert-butyl-pyridinium-methyl)phenyl-amino)-3-oxopropyl)-4-(3,4-dihydroxybenzamido)heptanediamide tribromide (19), and N1,N7-bis(3,5-bis(4-tert-butyl-pyridium-methyl)phenyl)-4-(3-(3,5-bis(4-tert-butyl-pyridinium-methyl)phenylamino)-3-oxopropyl)-4-(3,4-dihydroxybenzamido)heptanediamide hexabromide (20), and their facile binding to zinc oxide (ZnO) nanostructures is introduced.
- , , , , , , :
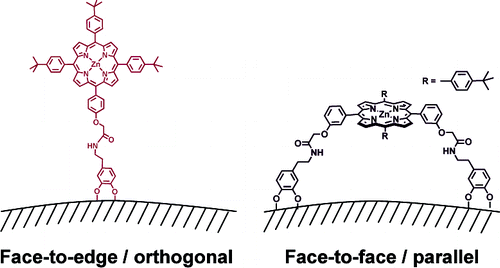
Grafting porphyrins (face-to-edge/orthogonal versus face-to-face/parallel) to ZnO en route toward dye-sensitized solar cells
In: Journal of Physical Chemistry B 114 (2010), p. 14671-14678
ISSN: 1520-6106
DOI: 10.1021/jp102737a
Novel types of binding motives have been investigated within the context of sensitizing ZnO-based dye-sensitized solar cells with metalloporphyrins. In particular, a complementary class of metalloporphyrin has been synthesized to probe the impact of a face-to-edge/orthogonal versus face-to-face/parallel orientation of the metalloporphyrin with respect to ZnO and has been compared to TiO2-based dye-sensitized solar cells. Our studies provide a deep and detailed understanding of the individual electron-transfer processes at the ZnO/metalloporphyrin interface, that is, electron injection, recombination, and dye regeneration, by means of steady-state and time-resolved techniques. Interestingly, we found that for our novel ZnO/metalloporphyrin systems, the injection efficiencies are close to unity, despite their long, nonconjugated anchoring group length.
- , , , , :
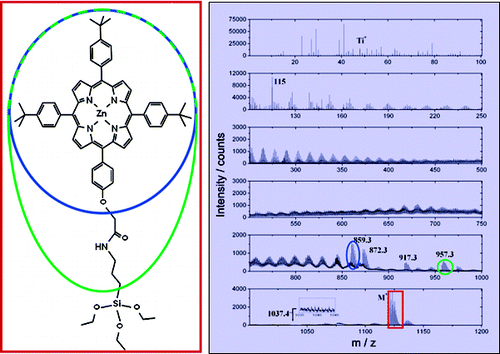
ToF-SIMS and XPS studies of the adsorption characteristics of a Zn-porphyrin on TiO2
In: Langmuir 26 (2010), p. 3531-3538
ISSN: 0743-7463
DOI: 10.1021/la9032139
Time-of-flight secondary ion mass spectrometry (ToF-SIMS) and X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS) were used to study monolayers (ML) and thick films of porphyrin Zn-TESP (C67H75N5O5SiZn) attached to titanium dioxide (TiO2) substrates via silanization. Films on ideal hydroxyl-terminated silicon (SiO2) surfaces were used for comparison. ToF-SIMS and XPS spectra show that the type of adsorption varies depending on the thickness of the organic film, the preparation temperature, and the adsorption time. We show that the intensity of a molecular peak at mass 1121.5 u in ToF-SIMS can be used as a direct measure of the ratio of chemisorption/physisorption of Zn-TESP. On TiO2, the amount of chemisorbed porphyrin can be increased by increasing the reaction temperature and time during the silanization process.
Communication via electron and energy transfer between zinc oxide nanoparticles and organic adsorbates
In: Journal of Physical Chemistry C 113 (2009), p. 4669-4678
ISSN: 1932-7447
DOI: 10.1021/jp810696h
Stable ZnO nanoparticles suitable for further surface functionalization were synthesized in the liquid phase from homogeneous ethanolic solutions of the precursors lithium hydroxide and zinc acetate. It was found that the growth of the particles was governed by temperature as well as the presence of the reaction byproduct lithium acetate during the aging process. In particular, the reaction could be almost completely arrested by removal of this byproduct. The “washing” consisted of repeated precipitation of the ZnO particles by addition of alkanes such as heptane, removal of the supernatant, and redispersion in ethanol. Furthermore, the surface of the colloidal ZnO nanoparticles was successfully modified by catechol-anchoring group containing dye molecules for the study of photochemical properties.